By 2024, there will be nearly 3 million unfilled cybersecurity positions, making it vital that you stand out from the crowd when you go to your next interview. In order to give yourself the best chance of impressing your future employer with your knowledge and expertise, you’ll need to prepare ahead of time by learning these 30+ Cybersecurity Interview Questions. Practice answering them during mock interviews and get ready to impress during the real interview!
In order to prepare for Cyber Security Jobs, let’s break this blog up into three parts: Beginner Questions, Intermediate Questions, and Advanced Questions. We will start with an introduction to cybersecurity.
Introduction
In the past few years, there has been an exponential increase in cyber attacks. In 2017, for example, 2 billion data records were stolen from US companies alone. This is only going to get worse as more and more people use the internet every day and everything from credit cards to personal emails is increasingly at risk of being hacked. With this increasing demand for Cybersecurity Professionals and higher-than-ever stakes for success, it’s more important than ever that you ace your next interview.
10 Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners
Is this your first interview for a cybersecurity position? Then you should prepare and be prepared for the interview process. You can get in there by answering these 10 Beginner Questions (Entry Level).
Question 1: What do you mean by Cybersecurity?
Answer: Cybersecurity is the act of protecting networks, data, and devices from cyber criminals. The US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) defines cybersecurity as the collection and analysis of information about actual or potential attacks or intrusions on computer systems and networks.
Cybersecurity can be viewed as a combination of people, processes, and technology used to protect valuable digital assets.
Question 2:What is the primary goal of Cybersecurity?
Answer: A primary goal of cybersecurity is to prevent unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of information. It also includes preventing improper authorized access to information systems that could result in physical harm to people.
Question 3:Define threat in cybersecurity.
Answer: A threat is anything that could potentially damage your company’s information and data. Threats can range from sabotage to theft, or even a natural disaster. There are countless types of threats that companies face every day. It’s important for cybersecurity professionals to be aware of the most common ones and how they can protect their company from them.
Question 4:What is vulnerability in Cybersecurity?
Answer: A vulnerability is a weakness that may be exposed by a system’s design, implementation, operation, or management. Some vulnerabilities are known and documented, while others are not. Vulnerabilities can also exist because of human error or other contingencies.
Build Your Career as a
Cyber Security Specialist
- Live Projects
- Resume / Interview Preparation

Question 5:What is Risk in Cybersecurity?
Answer: Cybersecurity is a multifaceted field that requires you to be aware of the risks, threats, and vulnerabilities that come with the territory.
Risk = Likelihood of a threat * Vulnerability Impact
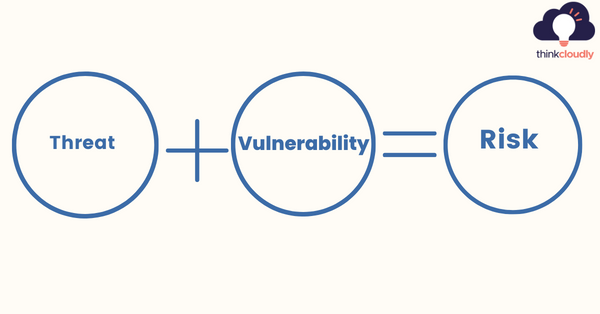
The most common types of risk are privacy, denial of service, and information leakage.
Privacy is a risk when users’ private data may be exposed or used without their knowledge.
Denial-of-service is a risk when hackers cause systems or networks to crash by overloading them with fake traffic.
Information leakage occurs when sensitive data is revealed unintentionally, such as passwords being posted publicly on social media sites.
All three of these can lead to disastrous consequences for those involved, so it’s important to do everything possible to minimize those risks before they occur!
Question 6: What is SSL?
Question 7:What is XSS?
Question 8:What does RDP stand for?
Question 9:What is a Firewall?
Question 10: What is a phishing attack, and how can it be prevented?
10 Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers for Intermediates
Question 1:Explain Cryptography in Cybersecurity.
Question 2:What is traceroute in Cybersecurity?
Question 3: What is Cross-Site Scripting and how it can be prevented?
To prevent XSS, developers need to verify any input they receive and make sure it doesn’t come from an untrusted source. This requires developers to validate the data before displaying it on their site. You could also use browser plugins like NoScript or Disconnect to block JavaScript execution in all third party pages.
Question 4: Name the elements of CyberSecurity.
Answer:
- Information security
- Network security
- Operational security
- Application security
- End-user education
- Business continuity planning
Question 5:What is Cyber Crime? Name some common Cyber Crimes.
Answer: Cybercrime is any crime that is committed using a computer or any other electronic device. Common forms of cybercrime include hacking, phishing, and malware.
You can protect yourself from these crimes by using strong passwords, installing antivirus software, not clicking on suspicious links, and being cautious with your personal information.
Below are some common Cyber Crimes:
- Identity Theft
- Online Predators
- Hacking of sensitive information from the Internet
- BEC (“Business Email Compromise”)
- Ransomware
- Stealing intellectual property
Question 6:What is the difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption in Cyber security?
Answer:
- The first difference is that symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, whereas asymmetric encryption uses a different key for each of those functions.
- The second difference is that symmetric encryption is faster than asymmetric encryption, but it can only be used to encrypt data of a set size. Asymmetric encryption can be used on any size of data. In addition, as mentioned before, asymmetric encryption uses two keys instead of one which adds another layer of security.
- Finally, asymmetric encryption offers more flexibility since one key cannot decrypt the other’s encoded message; thus if one key gets compromised there is still protection for all messages using the other key.
Boost your earning potential with Cyber Security expertise. Explore our certified Cyber Security courses for a high-paying career
Question 7:What are some examples of malware?
Answer: Malware is a term that encompasses a variety of malicious software. This includes viruses, trojan horses, worms, and ransomware. Malware is typically found on computers and other devices connected to the internet. Some examples of malware include:
Question 8:How can you protect yourself from malware?
Answer: Malware comes in many forms and can be hard to detect, but here are some ways you can protect yourself:
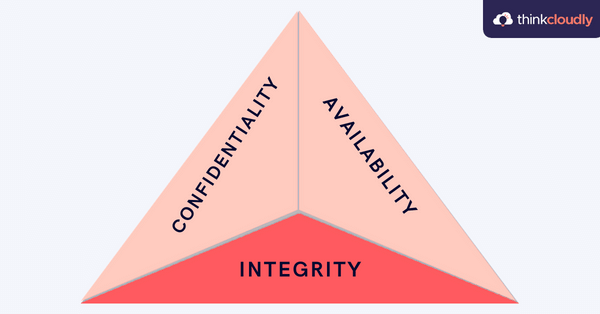
Question 9:What is the CIA triad?
Question 10:Define VPN.
10 Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers for Experts (Senior-Level)
We will discuss some common questions and answers for Cybersecurity interviews in this section.
Question 1:What is the difference between IDS and IPS?
Answer: An IDS (Intrusion Detection System) monitors the network for anomalies, while an IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) protects the system by preventing attacks. In other words, an IDS is reactive and an IPS is proactive. Both have their strengths and weaknesses. For example, an IDS has a better detection rate than an IPS but can’t prevent attacks like the IPS can. Conversely, the IPS can identify malicious traffic before it reaches its target but isn’t as accurate as an IDS. As such, many companies rely on a mix of both systems to cover any potential gaps in protection.
The key takeaway here is that you need both types of systems and then decide which one should be your primary focus depending on your company’s specific needs.
Question 2:What is the difference between hashing, encoding, and encrypting?
Answer: Hashing, encoding, and encrypting are all methods for securing data.
- Encoding is the process of converting raw data into a form that can be transmitted over a network or stored on a disk.
- Encrypting is the process of transforming encoded data into a form that can be read only by those with access to the appropriate key.
- Hashing is a one-way encryption method used for verifying input integrity, but not secrecy. A message digest is generated from an input string (e.g., hello) using a hashing algorithm (e.g., MD5). If the same string is entered again, it should produce the same hash value as before. The two strings should also have identical hash values if they’re identical copies of each other (e.g., hello = hello). However, if one character changes in either string (e.g., hello = hellp), then their hashes will be different.
Question 3:Who are Black Hat, White Hat and Grey Hat Hackers?
Question 4:How Would You Keep a Server and Network Secure?
- A strong firewall is the first line of defense against cyber security threats. If you have a weak firewall, hackers can easily access your data and steal it. This is why it’s important to make sure that your firewall software is up-to-date and configured properly.
- You should also install antivirus software on all of your devices, including laptops and smartphones, as this will provide added protection for any data leaks or malware.
- Another thing you need to do is create different passwords for each device so if one gets compromised, other devices are still secure.
- And finally, you should turn off wireless connections when they’re not in use to avoid them being hacked.
Question 5:What is two-factor authentication and how it can be implemented for public websites?
Answer: Two-factor authentication is a method of confirming the identity of a person through two means. One factor would be something they know, such as their password. The second factor is something they have, such as their mobile phone.
In this case, if someone tried to log into your account from an unknown location (a public computer or network), you would receive a text message with an access code that needs to be entered before you can log in and use your account. Even though this system seems simple, it has helped thwart many hacking attempts because it requires attackers to steal both parts of the security puzzle—something they know (your password) and something they have (your mobile device).
How does encryption work?: Encryption is a process used for securing data by converting readable information into unreadable form using cryptographic techniques. It helps in protecting confidential information like personal data, credit card numbers etc., from unauthorized persons.
Question 6:What is data leakage?
Answer: Data leakage is a cyber-security term that refers to the unauthorized transfer of data from one system, device, or network to another. The data could be anything from an email containing sensitive information, a confidential file on your laptop, or a customer’s credit card number.
- It can happen through hacking, social engineering techniques like phishing and keylogging, or by simply losing your phone.
- When you create passwords for your accounts, it is important to use complex passwords (letters, numbers) and change them regularly.
- You should also never click links in emails from unfamiliar sources or open attachments from people you don’t know as this could lead to malware infections or credential theft.
Question 7:What are the Types of data leakage?
Question 8: Explain brute force attacks and the ways to prevent it.
Answer: Brute force attacks are a type of hacking that involves systematically guessing passwords and other key data by testing every possible combination. This technique can be used for both breaking into networks and gaining access to individual user accounts. To prevent brute force attacks from happening, a strong password should be created that is at least 8 characters long, with a mix of upper-case letters, lower-case letters, numbers, and symbols. It’s also important to keep your password private; don’t write it down or store it on your computer.
Question 9: What Anomalies Do You Typically Look for When a System Becomes Compromised?
Answer: This is a difficult question. Interviewers want to know if they can think creatively and outside the box when there are no answers readily available. A good answer might be When a system becomes compromised, I typically look for any evidence of user or administrator access that should not be present. If anything looks out of place, it would be worth looking more closely into. I also look for any changes in file permissions on system files or directories as well as evidence of changes in firewall rules, host-based intrusion prevention systems (HIPS), or other protections put in place by the system’s administrators.
- Define an anomaly.
- Discuss why it’s important to catch anomalies in a compromised system.
- Describe a time when you identified an anomaly. What did you do?
Question 10: How Would You Monitor and Log Cyber Security Events?
Answer: It’s important to show your Interviewer that you can keep track of security events when answering Cybersecurity Interview Questions. Your detail-oriented nature can be demonstrated here, which is a great opportunity.
When answering this question, be sure to explain the following:
- The tools and methods you use to monitor computer systems.
- The process you use for logging events.
- How logging cyber security events helps you understand them.
Final Thoughts:
The cybersecurity industry is booming and it’s not only for the people who have years of experience under their belt. The industry needs smart, young minds to keep up with the ever-changing threats. If you’re looking for a career change, this is a great place to start.










