In today’s digitally-driven world, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical field to protect sensitive information and infrastructure from malicious attacks. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, organizations across industries are recognizing the importance of investing in robust security measures. This blog post will delve into four key aspects of cybersecurity: facts, job roles after certification, job demand, and salaries. Let’s embark on an exploration of this exciting and dynamic field!
Cybersecurity Facts:
- Cybercrime is on the rise: The increasing reliance on digital technology and the interconnectedness of systems have contributed to the surge in cybercrime. Reports estimate that cybercrime costs the global economy trillions of dollars annually. From large-scale data breaches to ransomware attacks and identity theft, cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities.
- The skills gap: The demand for cybersecurity professionals far outweighs the available talent pool. This skills gap creates a significant opportunity for individuals looking to enter the field. Organizations are actively seeking skilled experts who can protect their networks, systems, and sensitive data from cyber threats. Pursuing a career in cybersecurity can lead to long-term job security and a rewarding career path.
- Constantly evolving threats: Cyber threats are highly dynamic and continually evolving. Hackers and malicious actors adapt their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to bypass security measures. As a result, cybersecurity professionals must remain proactive and continually update their skills and knowledge. Staying abreast of the latest trends, emerging threats, and defensive strategies is crucial for effectively countering cyber attacks.
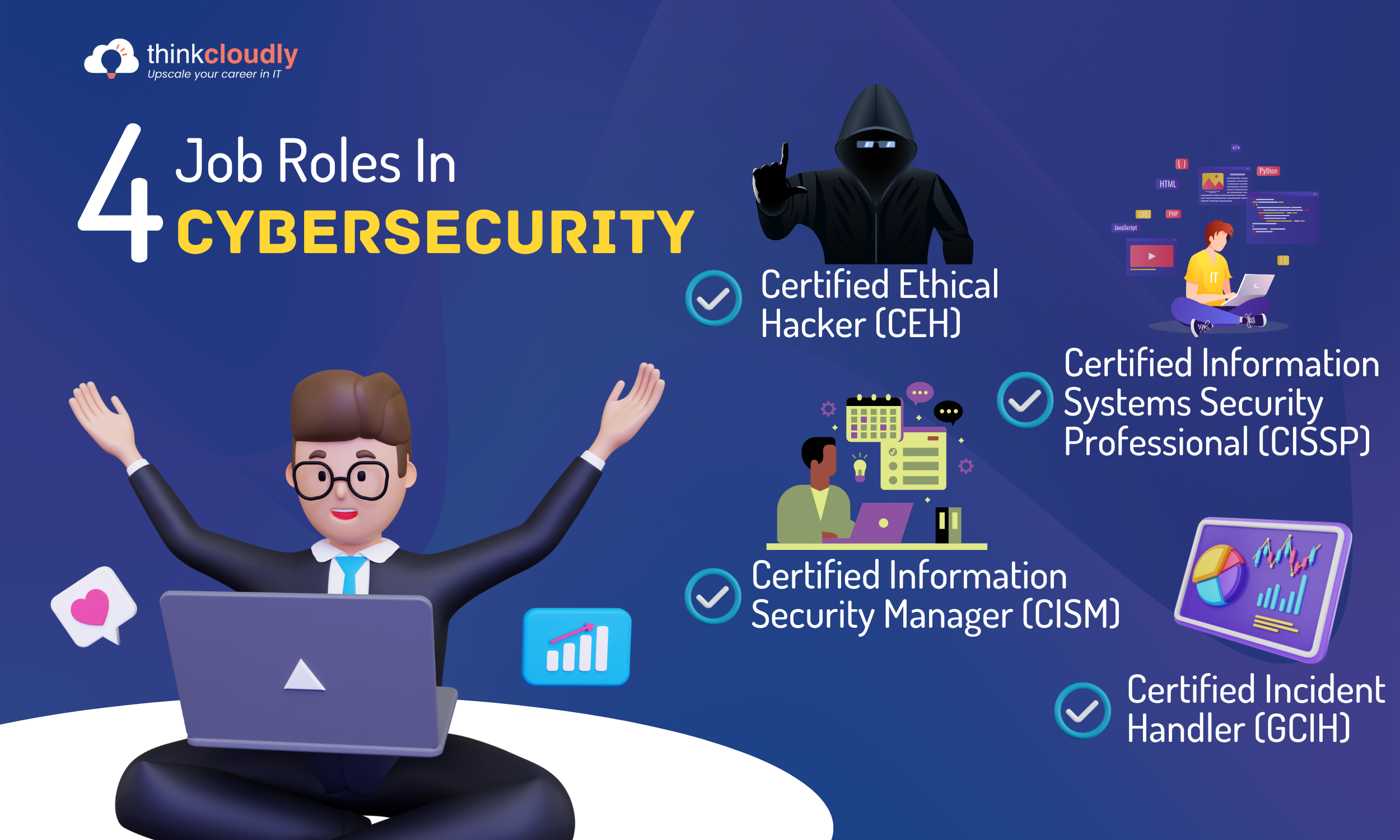
Cybersecurity Job Roles after Certification:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): CEH professionals are ethical hackers who use their skills to identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks. They conduct authorized penetration tests to assess an organization’s security posture and help implement remediation measures. CEH certification equips professionals with the necessary knowledge of hacking techniques, tools, and methodologies to protect systems from malicious attacks.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): CISSP-certified professionals are experts in designing, implementing, and managing security protocols and practices. They possess a broad understanding of various security domains, including access control, cryptography, security operations, and risk management. CISSP certification is highly regarded and is often required for senior-level positions in cybersecurity.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): CISM-certified individuals specialize in managing information security programs and aligning them with an organization’s business objectives. They are responsible for establishing and maintaining effective security governance frameworks, risk management strategies, and incident response plans. CISM certification demonstrates expertise in information security management and is beneficial for professionals aspiring to leadership roles.
- Certified Incident Handler (GCIH): GCIH professionals are skilled in responding to and investigating security incidents. They possess knowledge of incident handling methodologies, forensic techniques, and incident response best practices. GCIH certification equips professionals with the skills to effectively contain and mitigate the impact of security incidents and prevent future occurrences.
Boost your earning potential with Cyber Security expertise. Explore our certified Cyber Security courses for a high-paying career
Job Demand In Cybersecurity:
The listed surveys on Google show the job demand:
- The 2023 Cybersecurity Job Demand Survey states high job openings for cybersecurity professionals.
- Industry Perspectives survey results in a critical shortage of skilled cybersecurity experts, escalating demand.
- The Cybersecurity Employment Trends Survey proves the growing need and the surge in job postings in 2025.
- Job Market Analysis shows strong opportunities, and high demand for cybersecurity professionals by 2025.
The increased demand is due to:
- Increased cyber threats: The proliferation of cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and data breaches, has put organizations on high alert. The reputational and financial damages caused by successful cyber attacks have made cybersecurity a top priority for businesses. As a result, there is a growing demand for cybersecurity professionals who can protect sensitive information and mitigate risks.
- Regulatory compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies have enacted stringent data protection and privacy regulations. Compliance requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), necessitate robust cybersecurity measures. Organizations must ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of personal and sensitive data. Compliance-driven demands for cybersecurity professionals are expected to continue rising.
- Digital transformation: The rapid adoption of cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and other emerging technologies has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. As organizations embrace digital transformation, they require cybersecurity professionals who can secure these new technologies and address the associated risks. Protecting cloud environments, securing IoT networks, and implementing strong cybersecurity measures for digital infrastructure are key areas of job demand.
Cybersecurity Specialist Salary:
- Information Security Analyst: Information security analysts play a critical role in safeguarding organizations’ systems and data. They assess vulnerabilities, monitor networks for suspicious activities, and develop security protocols. The average salary for information security analysts ranges from $70,000 to $120,000 per year, depending on factors such as experience, location, and industry.
- Ethical Hacker: Ethical hackers, also known as penetration testers, use their skills to identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks. They perform authorized hacking attempts to assess an organization’s security posture and provide recommendations for improvement. Ethical hackers earn an average salary of $80,000 to $130,000 per year, depending on experience and expertise.
- Security Engineer: Security engineers are responsible for designing and implementing security solutions to protect networks, systems, and applications. They develop and maintain firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols. The average salary for security engineers ranges from $90,000 to $150,000 per year, depending on experience and job responsibilities.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): CISOs are senior-level executives who oversee an organization’s cybersecurity strategy and ensure the implementation of effective security measures. They are responsible for managing risk, establishing security policies, and leading incident response efforts. The salary for CISOs can vary significantly based on factors such as organization size, industry, and location, but typically ranges from $150,000 to $250,000 or more per year.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity offers a vast range of opportunities for individuals looking to make a meaningful impact in protecting digital assets and combating cyber threats. By staying informed about the evolving threat landscape, acquiring relevant certifications, and pursuing specialized job roles, aspiring cybersecurity professionals can position themselves for a successful and rewarding career. Moreover, the increasing demand for experts and competitive salaries make it an enticing field to explore. So, if you have a passion for technology, problem-solving, and making a difference in the digital world, this career could be the perfect fit for you.




No comment yet, add your voice below!