Introduction
In the ever-changing environment of cloud computing, security is a top priority for organizations around the world. With major cloud service providers like Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS) dominating the market, organizations need to understand the nuances of their security services before making a cloud infrastructure selection. While Azure and AWS both prioritize security, they differ in several ways. Let’s take a look at eight key differences between Azure security vs AWS security.
Azure Security VS Aws Security
The main differences between Azure security and AWS security are given below
1) Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Azure: Azure Active Directory (AD) is a complete identity and access management system with capabilities such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and conditional access restrictions.
- AWS: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) gives you precise control over user rights and access to AWS resources. It supports MFA and connects easily with other AWS services in cloud computing to enable centralized management.
2) Network Security
- Azure: Azure Virtual Network enables customers to create disparate networks and deploy network security groups (NSGs) to gain granular control over inbound and outbound traffic. Azure also provides DDoS prevention services.
- AWS : AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) allows customers to create virtual networks with specific IP address ranges. AWS provides network access control lists (ACLs) and security groups for traffic management, as well as DDoS mitigation services.
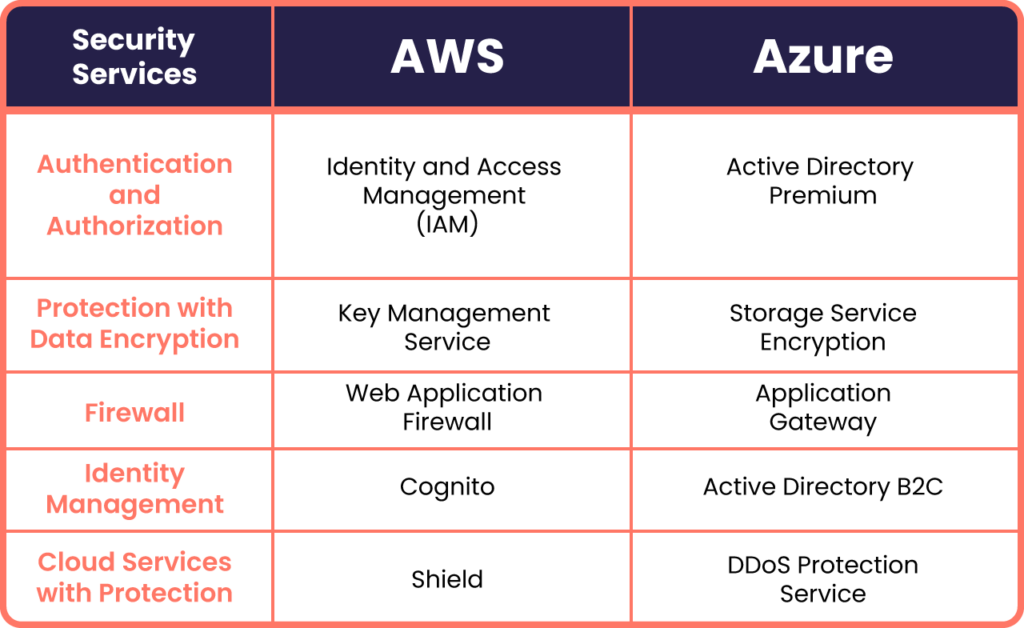
3) Encryption and Key Management
- Azure: Azure Key Vault enables the secure storage and management of cryptographic keys, certificates, and secrets. Azure provides encryption at rest and in transit using services such as Azure Disk Encryption and Azure Storage Service Encryption.
- AWS: AWS Key Management Service (KMS) enables customers to establish and manage encryption keys for data security. AWS also offers encryption at rest and in transit across many of its services, including Amazon S3 and Amazon RDS.
4) Compliance and Certifications
- Azure: Microsoft Azure services have various compliance certifications, including ISO 27001, SOC 1, SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR. Azure provides ample documentation and compliance resources to help organizations meet regulatory obligations.
- AWS: Amazon Web Services has a similar set of compliance certifications, including PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC 1, SOC 2, and GDPR. AWS provides compliance processes and documentation to help customers meet industry-specific standards.
5) Threat Detection and Monitoring
- Azure: Azure Security Center provides threat detection capabilities that use machine learning techniques to identify and remediate potential security risks. Azure Monitor enables comprehensive monitoring and logging of Azure resources.
- AWS: AWS Security Hub provides a consolidated view of security alerts and compliance status across multiple AWS accounts. AWS CloudWatch monitors and logs AWS infrastructure while continuously assessing resource configuration for AWS Configuration Security compliance.
6) Incident Response and Recovery
- Azure: Azure cloud service provides a variety of incident response tools and services, including automated response actions from the Azure Security Center and disaster recovery preparedness through Azure Site Recovery. Azure Backup simplifies data backup and recovery.
- AWS: Incident Response helps organizations prepare for and respond to security incidents by providing documentation, best practices, and incident response simulations. AWS Backup automates backup and recovery for AWS resources.
7) Serverless Security
- Azure: Azure Functions, Azure’s serverless computing service, leverages the threat detection features of Azure Security Center and connects to Azure Monitor for monitoring and reporting.
- AWS: AWS Lambda, AWS’s serverless compute solution, can be monitored and audited with AWS CloudWatch Logs and AWS CloudTrail to ensure visibility and compliance in serverless settings.
8) Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Azure: Azure Application Gateway includes WAF features to protect web applications from specific security risks while providing centralized management and real-time threat intelligence.
- AWS: AWS WAF is an online application firewall service that works with Amazon CloudFront and Application Load Balancer (ALB) to provide customizable rules to mitigate web-based attacks.
9) Native security integration with third-party solutions
- Azure: Azure Security Center works seamlessly with a variety of third-party security solutions and provides extensive APIs to enhance custom integrations, flexibility, and interoperability.
- AWS: Amazon web services Security Hub integrates seamlessly with a diverse set of third-party security products and services, allowing enterprises to easily combine security findings and automate remediation workflows.
Conclusion
While Azure and AWS both prioritize security and provide a wide range of capabilities to consolidate cloud environments, their approaches and implementations differ in many ways. It is important for enterprises to understand these differences to make informed decisions based on their specific security and regulatory compliance concerns. Businesses can create a robust and sustainable cloud architecture tailored to their specific security issues and goals by carefully evaluating the nuances of Azure and AWS security options.











No comment yet, add your voice below!