Introduction
As organisations continue to migrate their operations to the cloud, the importance of robust cloud security measures becomes paramount. The ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing brings forth opportunities and challenges, which require a proactive approach to safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining a resilient security posture. In this blog, we will explore the latest trends in cloud security and outline best practices that organisations can implement to protect their assets in the digital environment. Whether you’re an IT professional, a business owner, or someone simply curious about the dynamic world of cloud security, staying updated about the trends and adopting best practices is key to navigating the cloud securely.

Cloud Security Trends for 2024:
- Zero Trust Architecture:
Trend: The shift towards a Zero Trust Architecture, where no entry, whether inside or outside the organisation, is trusted by default.
Impact: Enhanced security as access permissions are granted based on authentication and verification, minimising the risk of unauthorised access.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR):
Trend: The integration of various security components into a unified platform for more effective threat detection and response.
Impact: Improved visibility into potential threats across cloud environments, enabling faster and more accurate incident response.
- Cloud-Native Security Solutions:
Trend: Increased adoption of security solutions specifically designed for cloud environments.
Impact: Tailored protection against cloud-specific threats, ensuring a more comprehensive defense strategy.
- Machine Learning and AI in Security:
Trend: Growing utilisation of machine learning and artificial intelligence for proactive threat detection and analysis.
Impact: More effective identification of anomalies and potential security incidents, reducing response time.
- DevSecOps Integration:
Trend: The integration of security practices into the DevOps process, fostering a culture of continuous security.
Impact: Enhanced collaboration between development, operations, and security teams, leading to more secure cloud deployments.
- Data Encryption and Privacy:
Trend: Increased focus on encrypting data both in transit and at rest, aligning with privacy regulations.
Impact: Strengthened data protection measures, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with privacy standards.
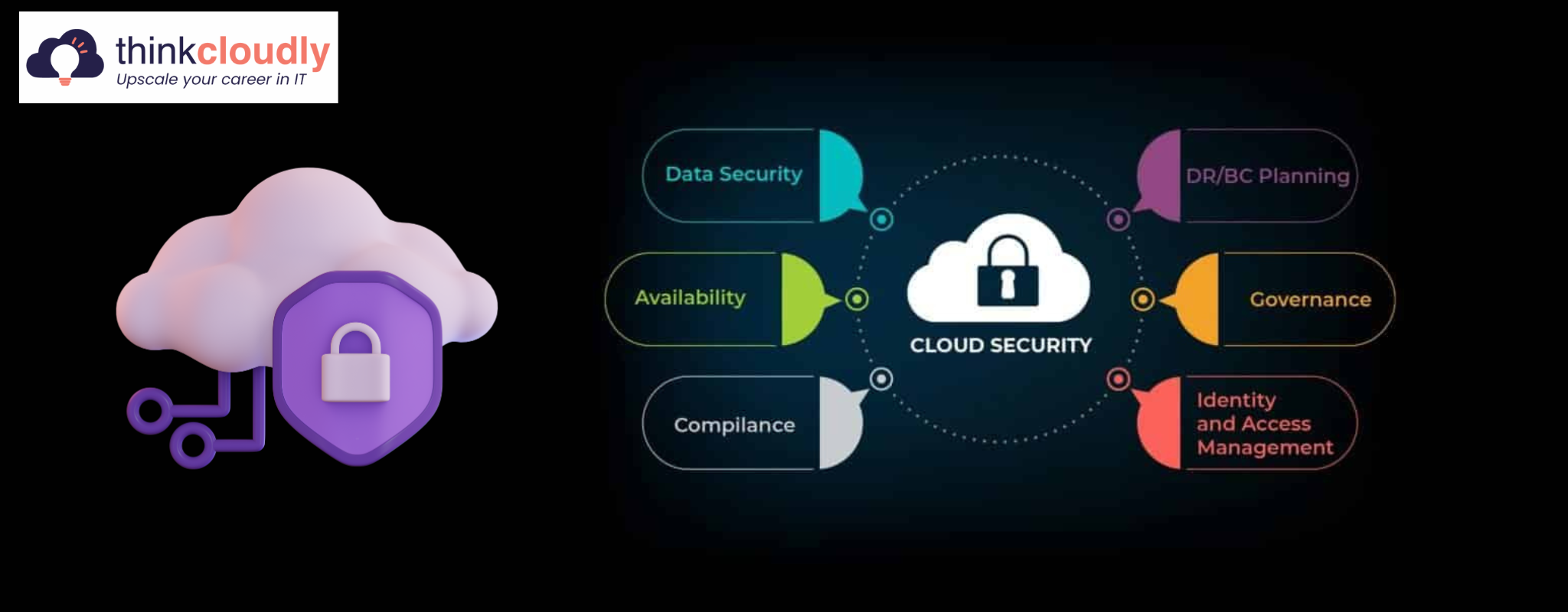
Best Practices for Cloud Security:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Practice: Enforce MFA for all users accessing cloud services to add an extra layer of identity verification.
Benefits: Mitigates the risk of unauthorised access, even in the event of compromised credentials.
- Regular Security Audits and Assessments:
Practice: Conduct regular audits and assessments of cloud infrastructure and configurations.
Benefits: Identifies potential vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, allowing for timely remediation.
- Continuous Monitoring:
Practice: Implement continuous monitoring of cloud environments for unusual activities or anomalies.
Benefits: Enables real-time threat detection and response, reducing the impact of security incidents.
- Data Classification and Encryption:
Practice: Classify data based on sensitivity and apply encryption to protect it.
Benefits: Safeguards sensitive information, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Employee Training and Awareness:
Practice: Provide comprehensive training to employees on cloud security best practices.
Benefits: Creates a security-aware culture, reducing the likelihood of human errors leading to security incidents.
- Regular Patching and Updates:
Practice: Keep cloud platforms, applications, and security solutions up-to-date with the latest patches.
Benefits: Addresses known vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of exploitation by cyber threats.
Cloud Security Interview Questions:
- What is Zero Trust Architecture, and how does it boost cloud security?
- Explain the concept of Extended Detection and Response (XDR) in the context of cloud security.
- How can organisations ensure the security of data in transit and at rest in a cloud environment?
- Discuss the role of machine learning and AI in improving cloud security.
- Why is the integration of security practices into DevOps important for cloud security?
- What measures can be taken to enforce multi-factor authentication for cloud services?
- How does continuous monitoring contribute to effective cloud security?
- Explain the significance of data classification and encryption in cloud security?
- Explain the significance of data classification and encryption in cloud security.
- What are the key benefits of regular security audits and assessments in a cloud environment?
- How can organisations foster a security-aware culture among employees to enhance security?
Conclusion
As cloud adoption continues to surge, staying ahead of the curve in terms of security is imperative. The identified trends and best practices outlined in this guide offer a roadmap for organisations and professionals seeking to fortify their cloud security posture in 2024. By embracing a proactive approach, leveraging advanced technologies, and adopting robust security measures, businesses can confidently navigate the cloud landscape while safeguarding their digital assets from evolving cyber threats. As cloud security becomes an integral part of the digital ecosystem, adherence to best practices and staying informed about emerging trends will be key to maintaining a resilient defence against potential threats.











No comment yet, add your voice below!